Fake news detection - Text Classification approach
02 Dec 2018 by dzlabFake news can belong to one of the following categories 1: a news which is intentionally false (i.e. a serious fabrication), hoaxes (i.e. created with the intent to go viral on social media networks) or articles intended as humor or satire. Here is sample legitimate and crowdsourced fake news in the Technology domain 2
| Legitimate | Fake |
|---|---|
| Nintendo Switch game console to launch in March for $299 The Nintendo Switch video game console will sell for about $260 in Japan, starting March 3, the same date as its global rollout in the U.S. and Europe. The Japanese company promises the device will be packed with fun features of all its past machines and more. Nintendo is promising a more immersive, interactive experience with the Switch, including online playing and using the remote controller in games that don’t require players to be constantly staring at a display. Nintendo officials demonstrated features such as using the detachable remote controllers, called ”Joy-Con,” to play a gun-duel game. Motion sensors enable players to feel virtual water being poured into a virtual cup. | New Nintendo Switch game console to launch in March for $99 Nintendo plans a promotional roll out of it’s new Nintendo switch game console. For a limited time, the console will roll out for an introductory price of $99. Nintendo promises to pack the new console with fun features not present in past machines. The new console contains new features such as motion detectors and immerse and interactive gaming. The new introductory price will be available for two months to show the public the new advances in gaming. However, initial quantities will be limited to 250,000 units available at the sales price. So rush out and get yours today while the promotional offer is running. |
The task of detecting fake news requires the application of NLP algorithm to search for patterns or linguistic constructs that could be used to flag an article as fake news. This task is different form fact checking which involves cross-referencing articles with other articles to look for inconsistency in the given information.
An algorithm for detecting fake news with an accuracy that outperform those of humans is a cutting edge AI work. As it involves not only the detection of non-fake news, but also the capabilities of verifying the ground-truth, and accounting for factors such as developing news and language and cultural interpretations.
In the following we address Fake News detection with a Text Classification approach that simply uses an NLP algorithm to parse sentence structure and hone in on keywords to classify news based on a training set with flaged fake and non fake articles content.
Data
The problem with the Fake News detection is that there is not enough data, a collection of articles with speific requirements that constitues a fake news corpus. What researshers usually do is constructing a dataset by crowd-sourcing fake news articles (e.g. through Amazon Mechanical Turk workers).
Fake news Datasets:
The following are some commonly available datasets for training NLP algorithms to detect fake news:
- BuzzFeedNews Facebook fact check dataset - link
- kaggle dataset
- Kagle competition using news headlines in chineese and english (translated) - link
Preprocessing:
Will be using this dataset. After downloading and un-zipping the file, load it into a dataframe to have a look:
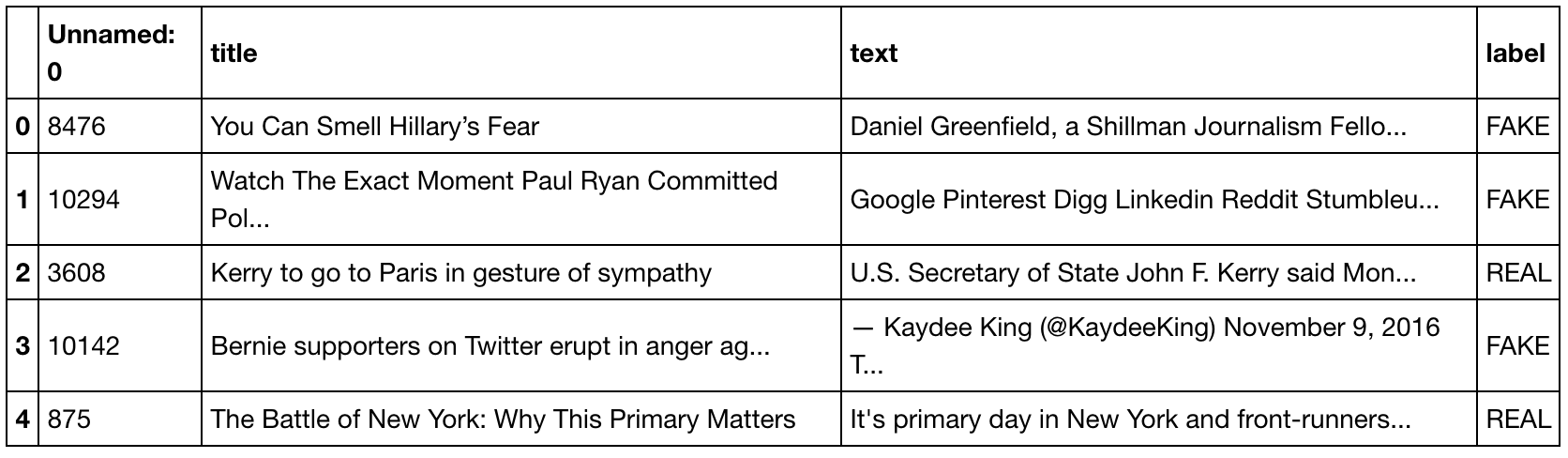
The first thing we need to do is tranform those articles into something that can be processed by computers throught two differents steps:
- Tokenization: split the original sentences into tokens (i.e. words). For example, spliting on spaces, properly handle punctuation, clean the text (e.g. remove HTML tags), separate compound word (e.g isn’t, don’t) in to different words.
- Numericalization: convert the tokens into integers by creating a vocabulary (i.e. list of all the words in the corpus). The size of the vocabulary should be limit (e.g. to 60,000) and contains only useful words (e.g. tokens that appear at least twice). Unfrequent words can be replaced by the unknown token UNK.
Those operation as performed by the folloing simple command (this can be slow):
TextClasDataBunch.load(path)Language model
A language model is a model trained to guess the next word starting from a sequence of words as input. It has a recurrent structure and a hidden state that is updated each time it sees a new word. This hidden state thus contains information about the sentence up to that point. Check this article for more details on how to train a language model from scratch.
Training
We need to train a model that classifies the news from scratch, starting from a model pretrained on a bigger dataset (wikitext-103 3). This pre-trained model catches a ‘knowledge’ of the English language which will be useful to our classifier.
But we should properly handle the specificity of our dataset. In fact, the English of the news in out dataset isn’t the same as the English of wikipedia, we need to adjust a the parameters of our model. Furthermore, words that could be very common in our dataset may not be present in wikipedia, and as a result might not be in the vocabulary of the wikitext-103 model.
Therefore, before jumping on the classification we first need to fine-tune the pretrained model to our particular dataset. We will use a special TextDataBunch class for the language model that ignores the labels (fake vs. real), the training this model for several epochs as follows:
# load data for language model training
data_lm = (TextList
.from_csv(path, 'fake_or_real_news.csv', cols='text') # load text file
.random_split_by_pct(0.1) # randomly split and keep 10% for validation
.label_for_lm() # label the dataset specifically for lnaguage modeling
.databunch(bs=48))
# create a learner and loat the weights of wikitext-103
learn = language_model_learner(data_lm, pretrained_model=URLs.WT103_1, drop_mult=0.3)
# look for a good good learning rate to pick
learn.lr_find()
learn.recorder.plot(skip_end=15)
# train the head of the model for one epoch
learn.fit_one_cycle(1, 1e-2, moms=(0.8,0.7))
# train all layers of the model for some time
learn.unfreeze()
learn.fit_one_cycle(20, 1e-3, moms=(0.8,0.7))
# save the model as an encoder to use later in the classifier
learn.save_encoder('fine_tuned_enc')The following figures depicts the training history which takes several hours to finish:
Prediction
After that the model is trainined on our dataset, we can try generate news as follows:
TEXT = "health"
N_WORDS = 40
N_SENTENCES = 2
print("\n".join(learn.predict(TEXT, N_WORDS) for _ in range(N_SENTENCES)))The output should look like this:
Total time: 00:02
Total time: 00:02
health care group , and habit of course , it a clear blank documentation on the xxmaj congress defining on fire troop transfer rust care growing discovers that ’s contained , in xxmaj new xxmaj january , the economy and what
health care , the xxmaj established to xxmaj israel wanted to the xxup u.s.
xxup u.s.
xxmaj stein issues like xxmaj intermediate - indecent or both xxmaj presidential proportionally , showing up recently released by xxmaj the xxmaj february
Classifier
After training a language model on our fakenews dataset, we can use this model to extract features from the articles and use them as a classification attributes.
# load the dataset for classification
data_clas = (TextList.from_csv(path, 'fake_or_real_news.csv', cols='text', vocab=data_lm.vocab)
.random_split_by_pct(valid_pct=0.1)
.label_from_df(cols='label')
.databunch(bs=bs))
# create a classifier and load the previously trained language model
learn = text_classifier_learner(data_clas, drop_mult=0.5)
learn.load_encoder('fine_tuned_enc')
learn.freeze()
# look for a good learning rate
learn.lr_find()
learn.recorder.plot()
# train the classifier
learn.fit_one_cycle(1, 1e-3, moms=(0.8,0.7))After several epochs, the accuracy of the classifier reaches 0.949447!
| epoch | train_loss | valid_loss | accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.168197 | 0.131191 | 0.949447 |
| 2 | 0.111397 | 0.220983 | 0.943128 |
Here is an example of classifly an article:
learn.predict("nonetheless , a republican - led congressional report called her decision “ premature , wrong and highly irresponsible . ” she was also criticized when facts emerged contradicting some of her earlier statements . \n the tribune post continued to discuss reno ’s position as a scapegoat : every day since she took office , she has been supervising at least")The output should look like this:
(Category FAKE, tensor(0), tensor([9.9990e-01, 1.0478e-04]))
Full notebook can be found here - link